The photos are a compilation of the work done on different crankshafts: R67/2, R60/2 and R69S.
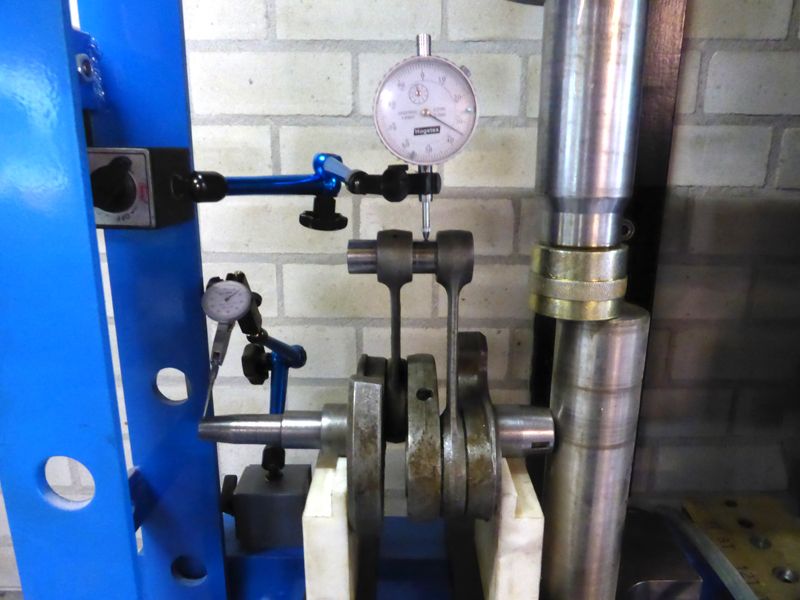

Before disassembling the crankshaft, it’s recommend to measure the out-of-round of the crankshaft outer ends, the crank pin alignment and the diameter of the main bearing journals (minimum 35.00 mm) More information on these measurements can be found at the end.
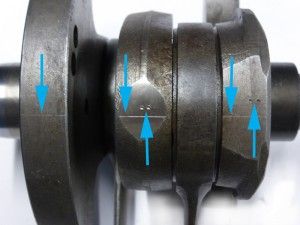
Use a scriber to draw a straight line on all 3 crank webs: this will be a usefull reference to align the crank webs during assembly. Mark the center web and 1 of the crank webs to assemble the webs in their original position.

Disassembly of the crankshaft: pressing the front crankpin.

While pressing, check the required pressure. It’s not unusual that >8 mt is required to losen the crank pin. After that, some 4 – 6 mt is normal for the first stage. The further the crank pin is pressed out, the lower the pressure required.

Front crank web pressed off

Pressing the rear crank pin

Front and rear crank web pressed off

Both crank pins stick out on the inside of the crank webs. It’s recommended to measure this. In this case (a factory original crankshaft) the crank pins extend some 1.35 mm

Pressing the crank pins out of the central crank web

Check all 4 crank pin seats in the 3 crank webs. Crankshafts that have been overhauled before, sometimes show deformations in the surface as a result of the skew pressing of the crank pin. This usually makes the crank web unserviceable.

In this case, the rear main bearing journal is undersized (34.95 mm)

This main journal got hard chrome plated and precision grinded to 35.00 mm with a k4 tolerance (+2 μm +9 μm)

On this crankshaft, the cone for the flywheel is in good condition. If this were not the case, it would need to be hardchromed as well.

BMW R69S crankshaft disassembled. With new conrods , cylindrical crank pins and roller bearings it’s ready for assembly. Note: R50, R60 and R69 crankshafts use tapered crank pins.

Comparative Rockwell hardness testing of the mid section of the old and new conrods: the used conrod tested 36HRC. The new conrods tested 46 – 47.5 HRC.

Both ends of the crank pin need to be rounded and polished, to prevent the crank pin to “bite” into the crank web.

Thoroughly clean crank pin and crank web. Apply anti seize compound (f.i. Molykote G-n Plus) on crank pin and crank web before assembly. DO NOT apply an anti seize compound with a high oil content on tapered crankpins. Use “Hirschtalg” or an equivalent product.

Align the holes of the oil feed along the centreline of the crank web, facing outwards.

Use a (hydraulic) vice clamp to align the crank pin and crank web. Press only up to +- 5 mm deep.

Continue pressing with an hydraulic press. Option: start with a small diameter press pin and a soft metal disk between the press pin and crank pin to prevent the crank pin from being pressed askew. Above ~3,000 kgs a bigger diameter press pin has to be used, to avoid pressing the cap further into the crank pin. At the end, the required pressure should be between 4,000 – 6,000 kgs. If not, something is wrong.

Keep monitoring the alignment while pressing the crank pin. (the 2nd pin, in this case).

When we received the crankshaft, it had already been disassembled……unfortunately without any alignment markings on the crank webs. Some crankshafts have a hole opposite the crank pin. With the use of a pin, a rough alignment can be obtained.


Pressing the front crank web. By regularly rotating the alignment pin, you can check whether the crank pin is going in straight. If it gets stuck, something is wrong…….

Continue pressing on the hydraulic press, while checking the alignment by regularly rotating the alignment pin.

The pressing must be continued on the other side of the crankshaft: the crank pin has a length of 53 mm while the total thickness of both crank webs and the conrod is less than 53 mm. The crank pin must protrude on the inside, to allow the oil slinger to lay flat against the crank web surface. Use a feeler gauge to set the axial play to a value between 0,07 and 0,10 mm. This is the original factory specification, However, nowadays some experts set the conrod axial play to 0.20 – 0.25 mm: this is to prevent the big end of the connecting rod from rubbing against the inside of the crank web due to the bending of the crankshaft under high load. This friction will generate (unwanted) extra heat. Note: some of the later R60/2 and R69S crankshafts came with thicker crank webs and used cylindrical crankpins with a length 54.5 mm.

Press rear crank web, following the same steps, except for the pre-pressing in a vice (use anti-seize compound, use alignment pin, set axial play to 0,07 – 0,10 mm).
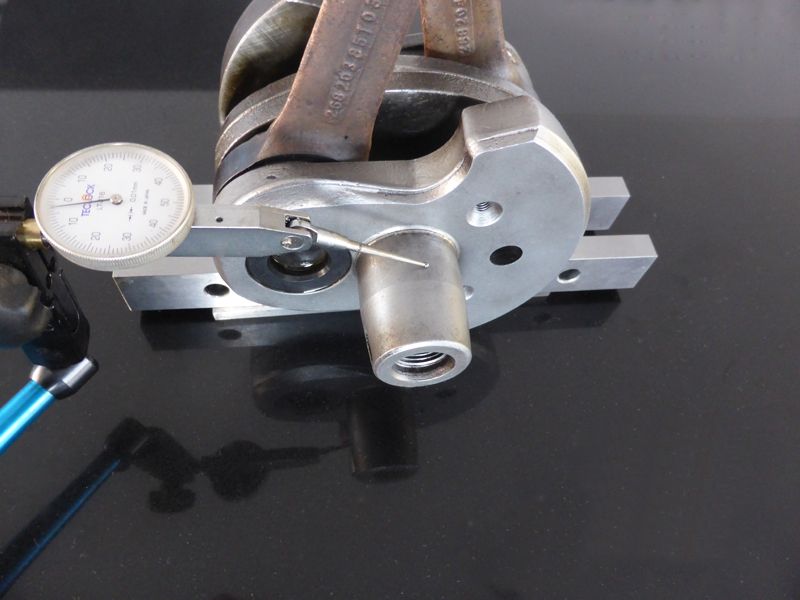

With the use of 2 parallels, the aligment of the crankwebs versus the center line of the crankshaft can be roughly checked. – measure the heigth of the main bearing journal – turn the crankshaft 180 degrees – again measure the height of the main bearing journal. A difference in value means that the crankweb is not aligned with the center line of the crankshaft and it tells you in which direction the crankweb needs to be rotated.

After assembly, the crank pin alignment and taper out-of-round needs to be measured. To get a good reading on the outer journal, any axial movement of the crankshaft needs to be eliminated, hence the steel rod on the right side.

With the use of a copper hammer, the crank webs can be rotated relative to each other. It requires some experience to understand where, how hard and which crank web to hit, in order to align the crank pins and at the same time true the tapers. This can be a tedious process, it sometimes needs up to 20 rounds of measuring & adjusting. Max. allowed out-of-round on crankshaft outer ends: 0.02 mm. Max. allowed misalignment of crank pins: 0.2 mm. See video below on how to measure the crank pin alignment. Some crankshafts that have been reconditioned before cannot be trued to the factory specs anymore, usually due to damaged crankpin bores in the crankwebs. Crankwebs with cylindrical crankpins typically have only 2 degrees of freedom: rotation and axial movement. In the case of conical crankpins, the crankwebs can tilt, which means that the crankwebs sometimes have to be wedged or pressed towards each other.
